# The adiabatic process equation (APE)
setClass(Class="Parcel",representation(T="numeric",Td="numeric",z="numeric",LCL="numeric"))
APE <- function(Parcel,z2){
DALR = -0.01
SALR = -0.006
# Calculate the LCL
LCL = (Parcel@Td-Parcel@T)/DALR+Parcel@z
Parcel@LCL = LCL
# Evaluate the APE and update the parcel temperature
Parcel@T = Parcel@T + min((LCL-Parcel@z),(z2-Parcel@z))*DALR + max(z2-LCL,0)*SALR
# Update the parcel's height and dewpoint if necessary
Parcel@z=z2
if(Parcel@z>=LCL){
Parcel@Td = Parcel@T
Parcel@LCL = Parcel@z}
return(Parcel)
}
A = new("Parcel",T=3,Td=-1,z=1484,LCL=NaN)
A = APE(A,A@z)
B = APE(A,2133)
C = APE(B,1550)
D = APE(C,832)Lecture Quiz 4
1
When the atmosphere is stable:
- A. Vertical movement of air parcels in encouraged
- B. Vertical movement of air parcels in suppressed
- C. All movement of air parcels in suppressed
- D. Air at the surface is warmer than the air above it
- E. Air at the surface is very cold
Answer:
- B. Vertical movement of air parcels in suppressed
2
Which type of conditions would be associated with the worst air quality (high pollution levels) down-wind of a coal-fired power plant?
- A. Unstable Conditions
- B. Conditionally Unstable Conditions
- C. Neutral Conditions
- D. Stable Conditions
- E. Very Windy Conditions
Answer:
- D. Stable Conditions
3
Figure 1 illustrates an example of:
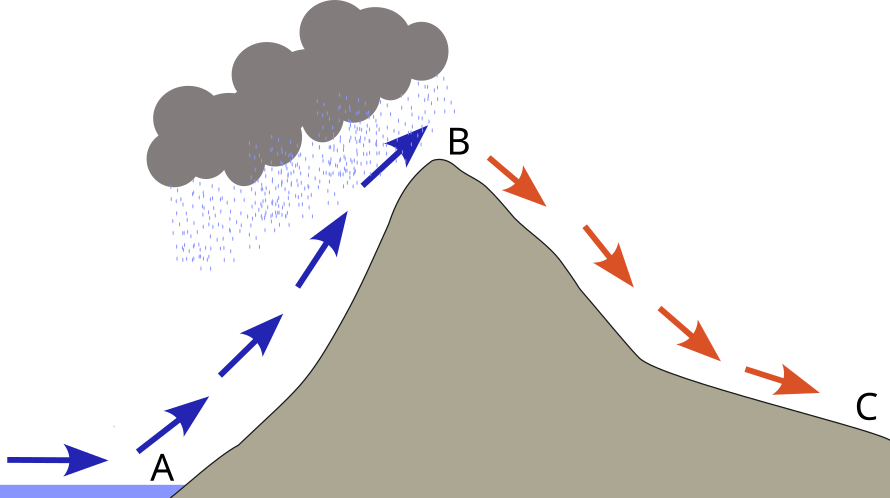
- A. Tectonic Uplift
- B. Orogenic Events
- C. Topography
- D. Topology
- E. Orographic Lift
Answer:
- E. Orographic Lift
4
In Figure 1, Parcel A is on the shore of garibaldi lake, with a surface elevation of 1484 m.a.s.l. with \(T\) = 3 \(^{\circ}\) C \(^{\circ}\) C and \(T_d\) = -1 \(^{\circ}\) C \(^{\circ}\) C. Assuming the DALR = -0.01 K m-1 and the SALR = -0.006 K m-1, what is the height of the LCL for parcel A?
- A. 1884 m.a.s.l
- B. 2133 m.a.s.l
- C. 1700 m.a.s.l
- D. 1484 m.a.s.l
- E. 1884 m.a.s.l
Answer:
- 1884 m.a.s.l
5
In Figure 1, location B represents the summit of panorama ridge, 649 m above the lake surface. If parcel A is blown up the slope, to location B, what would conditions at location B be like? Assume the DALR = -0.01 K m-1 and the SALR = -0.006 K m-1.
- A. Rain will be likely location B
- B. No precipitation will occur at location B because it is below the LCL
- C. Snow will be likely at location B
- D. There is not enough information to answer this question
- E. No precipitation will occur at location B because it is above the LCL
Answer:
- C. Snow will be likely at location B
6
In Figure 1, location C represents Helm Creek Campground, which has an elevation of 1550 m.a.s.l. Assume parcel A is blown up and over location B, then down to location C. What would the air temperature be at location C? Assume the DALR = -0.01 K m-1 and the SALR = -0.006 K m-1.
- A. Not enough information to answer the question.
- B. -2.494 \(^{\circ}\) C
- C. 3 \(^{\circ}\) C
- D. 3.336 \(^{\circ}\) C
- E. 10.516 \(^{\circ}\) C
Answer:
- D. 3.336 \(^{\circ}\) C
7
In Figure 1, location C represents Helm Creek Campground, which has an elevation of 1550 m.a.s.l. Assume parcel A is blown up and over location B, then down to location C. What would the dewpoint be at location C? Assume the DALR = -0.01 K m-1 and the SALR = -0.006 K m-1.
- A. Not enough information to answer the question.
- B. -2.494 \(^{\circ}\) C
- C. 3 \(^{\circ}\) C
- D. 3.336 \(^{\circ}\) C
- E. 10.516 \(^{\circ}\) C
Answer:
- B. -2.494 \(^{\circ}\) C
8
In the atmosphere ____ is more efficient than ____ at transporting heat energy.
- A. Diffusion,Convection
- B. Convection,Diffusion
- C. Advection,Convection
- D. Advection,Diffusion
- E. A, B, & C
Answer:
- Convection,Diffusion
9
Mechanical convection cane be generated by:
- A. Two layers of air passing one another with different velocities.
- B. Skin friction as an air parcel moves over a surface.
- C. Large obstructions blocking flow
- D. B & C
- E. A, B, & C
Answer:
- E. A, B, & C
10
Thermal convection:
- A. Is caused by surface heating
- B. Is more likely to occur during the day
- C. Requires a consistent supply of kinetic energy
- D. A & B
- E. A B & C
Answer:
- D. A & B
11
Would you like one free extra credit point? There are multiple correct answers, but you only need to select one.
- A. Yes!
- B. Absolutely!
- C. Of Course!
- D. Why Not?
- E. If it’s free, I’ll take it :)
Answer:
- A-E all get you a free point